Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Kenichi; Sekine, Daiki*; Sakiyama, Yuji*; Takahashi, Jun*; Takai, Kenichi*; Omura, Tomohiko*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48(79), p.30949 - 30962, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)To understand hydrogen embrittlement (HE), which is one of the stress corrosion cracking of steel materials, it is necessary to know the H distribution in steel, which can be effectively interpreted by numerical simulation of thermal desorption spectra. In weld metals and TRIP steels, residual austenite significantly influences the spectra, but a clear H distribution is not well known. In this study, an originally coded two-dimensional model was used to numerically simulate the previously reported spectra of high-carbon ferritic-austenitic duplex stainless steels, and it was found that H is mainly trapped at the carbide surface when the amount of H in the steel is low and at the duplex interface when the amount of H is high. It was also found that the thickness dependence of the H desorption peak for the interface trap site is caused by a different reason than the conventional one.
 3(111) and
3(111) and  5(0-13) grain boundaries of
5(0-13) grain boundaries of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metals, 12(4), p.662_1 - 662_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus atoms in steels accumulate at grain boundaries via thermal and/or irradiation effects and induce grain boundary embrittlement. Quantitative prediction of phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries under various temperature and irradiation conditions is therefore essential for preventing embrittlement. To develop a model of grain boundary phosphorus segregation in  -iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries (
-iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries ( 3[1-10](111) and
3[1-10](111) and  5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the
5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the  3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the
3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the  5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
Grund, J.*; Asai, Masato; Blaum, K.*; Block, M.*; Chenmarev, S.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Lohse, S.*; Nagame, Yuichiro*; Nagy, Sz.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Lohse, S.*; Nagame, Yuichiro*; Nagy, Sz.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 972, p.164013_1 - 164013_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.94(Instruments & Instrumentation)We report on the successful coupling of the Penning-trap mass spectrometry setup TRIGA-TRAP to the research reactor TRIGA Mainz. This offers the possibility to perform direct high-precision mass measurements of short-lived nuclei produced in neutron-induced fission of a  U target located near the reactor core. An aerosol-based gas-jet system is used for efficient transport of short-lived neutron-rich nuclei from the target chamber to a surface ion source. In conjunction with new ion optics and extended beam monitoring capabilities, the experimental setup has been fully commissioned. The design of the surface ion source, efficiency studies and first results are presented.
U target located near the reactor core. An aerosol-based gas-jet system is used for efficient transport of short-lived neutron-rich nuclei from the target chamber to a surface ion source. In conjunction with new ion optics and extended beam monitoring capabilities, the experimental setup has been fully commissioned. The design of the surface ion source, efficiency studies and first results are presented.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
In decommissioning sodium-cooled fast reactors, the operators can be exposed to radiation during dismantling of the cold trap equipment (C/T). The C/T has higher dose equipment because the C/T trapped the tritium of the fission product during the operation to purify the sodium coolant. In this research, the thermal decomposition temperature and rate of sodium hydride were measured as the fundamental research for improvement of the thermorlysis method prior to the dismantling. We measured the thermal decomposition temperature and rate using sodium hydride powder (95.3%, Sigma-Aldrich) in Al O
O crucible with TG-DTA (STA2500, NETASCH Japan). The heating rates were set to
crucible with TG-DTA (STA2500, NETASCH Japan). The heating rates were set to  = 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0 K/min, and the weight decrease was measured. The thermal decomposition temperature and rate were obtained from the temperature of the onset of the weigh decrease and the Kissinger plot, respectively. Furthermore, we set to the thermal decomposition temperature of around 600 K, and the weight decreasing rates were measured. The change of the chemical composition of the sodium hydride with heating (from NaH to Na) was measured with X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis. As a result, the thermal decomposition occurred at around 600 K, and the almost all hydrogen in the sodium hydride released within 1 h. The thermal decomposition rate strongly depended on the heating temperature.
= 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0 K/min, and the weight decrease was measured. The thermal decomposition temperature and rate were obtained from the temperature of the onset of the weigh decrease and the Kissinger plot, respectively. Furthermore, we set to the thermal decomposition temperature of around 600 K, and the weight decreasing rates were measured. The change of the chemical composition of the sodium hydride with heating (from NaH to Na) was measured with X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis. As a result, the thermal decomposition occurred at around 600 K, and the almost all hydrogen in the sodium hydride released within 1 h. The thermal decomposition rate strongly depended on the heating temperature.
 -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
TMS 2020; 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, p.995 - 1002, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:59.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus (P) is known as an element which causes grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steels. In addition, GB P segregation is promoted by the increase of vacancies and self interstitial atoms due to irradiation. Thus, the diffusion rate theory model for estimating irradiation-induced GB P segregation has been developed based on the atomic processes. Since the present model does not include the trapping and de-trapping processes at GBs, however, it cannot calculate the value which is directly compared with experimental results. In this study, we simulated the migration of a P atom in the  3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Keikinzoku, 68(11), p.596 - 602, 2018/11
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) is considered as one cause of stress corrosion cracking. HE is a serious problem in the development of high strength aluminum alloy as with steels. For understanding HE, it is inevitable to know hydrogen trapping states in the alloys and it can be identified using thermal desorption spectrometry of H. In this study, we numerically simulated thermal desorption spectra of hydrogen in aluminum for a cylindrical and a plate specimens and interpreted the desorption peaks included in them on the basis of the trap site concentration and the trap energy. As a result, we found that the peak at the lowest-temperature side can result from grain boundaries and confirmed that the reported interpretation for other peaks is reasonable. We also obtained the result showing the possibility that the trap site concentration of defects changes during heating the specimens. This result may give a suggestion for the interpretation of temperature desorption spectra of steels.
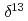 C and
C and 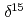 N values of sediment-trap particles in the Japan and Yamato Basins and comparison with the core-top values in the East/Japan Sea
N values of sediment-trap particles in the Japan and Yamato Basins and comparison with the core-top values in the East/Japan SeaKhim, B.-K.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Park, K.-A.*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
Ocean Science Journal, 53(1), p.17 - 29, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.64(Marine & Freshwater Biology)Distribution of carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios (
 C,
C, 
 N) in sinking particles collected in four stations in the Japan Sea was summarized. The
N) in sinking particles collected in four stations in the Japan Sea was summarized. The 
 C and
C and 
 N values in the sinking particles showed a clear seasonal variation, which agreed well with the variation in the chlorophyll a concentration in the surface seawater and in the sinking flux of biogenic particles. In particular, during the highly productive season of phytoplankton, a remarkable isotopic fractionation of
N values in the sinking particles showed a clear seasonal variation, which agreed well with the variation in the chlorophyll a concentration in the surface seawater and in the sinking flux of biogenic particles. In particular, during the highly productive season of phytoplankton, a remarkable isotopic fractionation of 
 N was found in the sinking particles, and it was inferred that the fractionation indicates the degree of nitrogen uptake by diatoms in the surface layer. These results are helpful information for linking the phenomenon in the ocean surface and the isotopic information recorded in the seafloor.
N was found in the sinking particles, and it was inferred that the fractionation indicates the degree of nitrogen uptake by diatoms in the surface layer. These results are helpful information for linking the phenomenon in the ocean surface and the isotopic information recorded in the seafloor.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.470 - 477, 2017/00
For understanding hydrogen (H) embrittlement of steels, it is necessary to infer the state that defects trap H in the steels. Thermal desorption spectra of H obtained by the thermal desorption spectrometry (TDS) are used for inferring such a state. Because the thermal desorption spectra include the influence of experimental conditions and hydrogen diffusion as well as information of the defects trapping H, it is necessary to interpret the spectra using the numerical simulation. In the presentation, we determined the detrapping and the trapping rate constants which are necessary for the simulation from the experimental spectra obtained for plate specimens which is so small that H diffusion is ignorable. Then we confirmed that the model using the obtained rate constants can simulate the spectra of larger cylindrical specimens, so that it was found that the rate constant for small specimens can be used for the simulation of the spectra for specimens of different shape or size.
Wakai, Eiichi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi*; Ito, Yuzuru*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yagi, Juro*; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 11, p.2405112_1 - 2405112_4, 2016/11
Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
, 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
Transport processes of particulate radiocesium obtained from a three year time-series sediment trap experiments at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant off Fukushima are expounded. Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material in sinking particles, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. In particular, we found that accident-derived radiocesium associate with slope and shelf sediments were resuspended and transported laterally to the offshore regions in typhoon seasons in 2013. Continuous observation of such transport processes of particulate radiocesium near the seabed would be significant for better understanding of the fate of accident-derived radiocesium.
Buesseler, K. O.*; German, C. R.*; Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Black, E. E.*; Kawakami, Hajime*; Manganini, S. M.*; Pike, S.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(16), p.9807 - 9816, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.54(Engineering, Environmental)A three year time-series of particle fluxes is presented from sediment traps deployed at 500 and 1000 m at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. The accident-derived radiocesium were enhanced in flux peaks that, given variations in trap  Cs/
Cs/ Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from
Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from  120 to
120 to  500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
 /p-AlInGaP solar cells
/p-AlInGaP solar cellsLee, H. S.*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*; Ekins-Daukes, N. J.*; Khan, A.*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 376-377, p.564 - 567, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.56(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Sato, Fumiatsu*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 404-406, p.288 - 292, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.6(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of ion irradiation on the rate of electrochemical hydriding rate of palladium (Pd) was investigated. In this study, ion irradiation onto the Pd surface was made with H , He
, He , Ar
, Ar and N
and N in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1
in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1  10
10 cm
cm . As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
. As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Noriki, Shinichiro*
Journal of Oceanography, 61(1), p.25 - 40, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:50.74(Oceanography)Settling particles play an important role in transport of organic carbon from the surface to the deep ocean. It is known that major components of settling particles are biogenic silicates (opal), biogenic carbonate, lithogenic clays and organic matters. In this study, we estimated organic carbon fluxes that are carried by each component in the western North Pacific Ocean (WNP) including the Japan Sea. Mean organic carbon flux at 1 km depth in the WNP (13.5 mg/m /day) was larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific (7.4), central North Pacific (1.1), Equatorial Pacific (4.2), Southern Ocean (5.8) and Eastern North Pacific (1.8). In the WNP, opal was a dominant component and 55 % of particulate organic carbon was carried by opal particles. Opal is known as a major component even in the Eastern North Pacific and Southern Ocean and opal fluxes in these areas are as much as in the WNP. However, organic carbon flux that was carried by opal particles in the WNP was significantly larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific and the Southern Ocean. It was cleared that opal particles in the WNP had great abilities not only to activate the biological pump in the surface ocean but also to transport organic carbon to the deep ocean.
/day) was larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific (7.4), central North Pacific (1.1), Equatorial Pacific (4.2), Southern Ocean (5.8) and Eastern North Pacific (1.8). In the WNP, opal was a dominant component and 55 % of particulate organic carbon was carried by opal particles. Opal is known as a major component even in the Eastern North Pacific and Southern Ocean and opal fluxes in these areas are as much as in the WNP. However, organic carbon flux that was carried by opal particles in the WNP was significantly larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific and the Southern Ocean. It was cleared that opal particles in the WNP had great abilities not only to activate the biological pump in the surface ocean but also to transport organic carbon to the deep ocean.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review Letters, 93(20), p.200402_1 - 200402_4, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:74.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Pb in the northwestern Japan Sea
Pb in the northwestern Japan SeaOtosaka, Shigeyoshi; Baba, Masami*; Togawa, Orihiko; Karasev, E. V.*
Pacific Oceanography, 1(2), p.149 - 157, 2003/12
A sediment trap experiment and sediment coring were carried out in the northwestern Japan Sea (Sta MS), and lead-210 ( Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of
Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of  Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of
Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of  Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of
Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of  Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of
Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of  Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large
Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large  Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of
Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of  Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate
Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate  Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Sengoku, Seio
Denki Gakkai Purazuma Kenkyukai Shiryo (PST-03-41), p.23 - 26, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
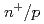 -InGaP space solar cells
-InGaP space solar cellsDharmarasu, N.*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*; Bourgoin, J. C.*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Matsuda, Sumio*
Applied Physics Letters, 81(1), p.64 - 66, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:55.81(Physics, Applied)We studied the properties of observed defects in n /p-InGaP solar cells created by irradiation of protons with different energies.Three majority (hole) and a minority-carrier traps, labeled respectively as HP1 (E
/p-InGaP solar cells created by irradiation of protons with different energies.Three majority (hole) and a minority-carrier traps, labeled respectively as HP1 (E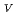 +0.90
+0.90 0.05eV), HP2 (E
0.05eV), HP2 (E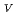 +0.73
+0.73 0.05eV), H2 (E
0.05eV), H2 (E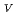 +0.55eV),and EP1 (E
+0.55eV),and EP1 (E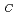 0.54eV),were identified using deep level transient spectroscopy. All majority-carrier traps were found to act as recombination centers. While the H2 traps present in the proton-irradiated p-InGaP was found to anneal out by minority-carrier injection, the other traps were not.
0.54eV),were identified using deep level transient spectroscopy. All majority-carrier traps were found to act as recombination centers. While the H2 traps present in the proton-irradiated p-InGaP was found to anneal out by minority-carrier injection, the other traps were not.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 43(12A), p.217 - 228, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:30.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Kamada, Yutaka; Suzuki, Takahiro; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Takeji, Satoru; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Hatae, Takaki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 87(8), p.085001_1 - 085001_4, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:183 Percentile:95.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English